音频重采样 ¶
译者:龙琰
项目地址:https://pytorch.apachecn.org/2.0/tutorials/beginner/audio_resampling_tutorial
原始地址:https://pytorch.org/audio/stable/tutorials/audio_resampling_tutorial.html
作者: Caroline Chen, Moto Hira
本教程展示如何使用 torchaudio 的重采样 API。
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.functional as F
import torchaudio.transforms as T
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
输出:
准备工作
首先,我们导入模块并定义辅助函数。
import math
import timeit
import librosa
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import resampy
from IPython.display import Audio
pd.set_option("display.max_rows", None)
pd.set_option("display.max_columns", None)
DEFAULT_OFFSET = 201
def _get_log_freq(sample_rate, max_sweep_rate, offset):
"""Get freqs evenly spaced out in log-scale, between [0, max_sweep_rate // 2]
offset is used to avoid negative infinity `log(offset + x)`.
"""
start, stop = math.log(offset), math.log(offset + max_sweep_rate // 2)
return torch.exp(torch.linspace(start, stop, sample_rate, dtype=torch.double)) - offset
def _get_inverse_log_freq(freq, sample_rate, offset):
"""Find the time where the given frequency is given by _get_log_freq"""
half = sample_rate // 2
return sample_rate * (math.log(1 + freq / offset) / math.log(1 + half / offset))
def _get_freq_ticks(sample_rate, offset, f_max):
# Given the original sample rate used for generating the sweep,
# find the x-axis value where the log-scale major frequency values fall in
times, freq = [], []
for exp in range(2, 5):
for v in range(1, 10):
f = v * 10**exp
if f < sample_rate // 2:
t = _get_inverse_log_freq(f, sample_rate, offset) / sample_rate
times.append(t)
freq.append(f)
t_max = _get_inverse_log_freq(f_max, sample_rate, offset) / sample_rate
times.append(t_max)
freq.append(f_max)
return times, freq
def get_sine_sweep(sample_rate, offset=DEFAULT_OFFSET):
max_sweep_rate = sample_rate
freq = _get_log_freq(sample_rate, max_sweep_rate, offset)
delta = 2 * math.pi * freq / sample_rate
cummulative = torch.cumsum(delta, dim=0)
signal = torch.sin(cummulative).unsqueeze(dim=0)
return signal
def plot_sweep(
waveform,
sample_rate,
title,
max_sweep_rate=48000,
offset=DEFAULT_OFFSET,
):
x_ticks = [100, 500, 1000, 5000, 10000, 20000, max_sweep_rate // 2]
y_ticks = [1000, 5000, 10000, 20000, sample_rate // 2]
time, freq = _get_freq_ticks(max_sweep_rate, offset, sample_rate // 2)
freq_x = [f if f in x_ticks and f <= max_sweep_rate // 2 else None for f in freq]
freq_y = [f for f in freq if f in y_ticks and 1000 <= f <= sample_rate // 2]
figure, axis = plt.subplots(1, 1)
_, _, _, cax = axis.specgram(waveform[0].numpy(), Fs=sample_rate)
plt.xticks(time, freq_x)
plt.yticks(freq_y, freq_y)
axis.set_xlabel("Original Signal Frequency (Hz, log scale)")
axis.set_ylabel("Waveform Frequency (Hz)")
axis.xaxis.grid(True, alpha=0.67)
axis.yaxis.grid(True, alpha=0.67)
figure.suptitle(f"{title} (sample rate: {sample_rate} Hz)")
plt.colorbar(cax)
重采样概述
要将音频波形从一种频率重新采样为另一种频率,可以使用 torchaudio.transforms.Resample 或 torchaudio.functional.resample()。 transforms.Resample 预先计算并缓存用于重采样的内核,而 functional.resample 则动态计算它,因此使用 torchaudio.transforms.Resample 将在使用相同参数重采样多个波形时加快速度(请参阅基准测试部分)。
两种重采样方法都使用带限正弦插值来计算任意时间步长的信号值。 实现涉及卷积,因此我们可以利用 GPU/多线程来提高性能。
Note
在多个子进程中使用重采样时(例如使用多个工作进程加载数据),您的应用程序可能会创建比系统能够有效处理的线程更多的线程。 在这种情况下,设置
torch.set_num_threads(1)可能会有所帮助。
由于有限数量的样本只能代表有限数量的频率,因此重采样不会产生完美的结果,并且可以使用多种参数来控制其质量和计算速度。 我们通过对对数正弦扫描重新采样来演示这些特性,这是一种频率随时间呈指数增长的正弦波。
下面的频谱图显示了信号的频率表示,其中 x 轴对应于原始波形的频率(以对数刻度表示),y 轴对应于绘制波形的频率,颜色强度对应于幅度。
sample_rate = 48000
waveform = get_sine_sweep(sample_rate)
plot_sweep(waveform, sample_rate, title="Original Waveform")
Audio(waveform.numpy()[0], rate=sample_rate)
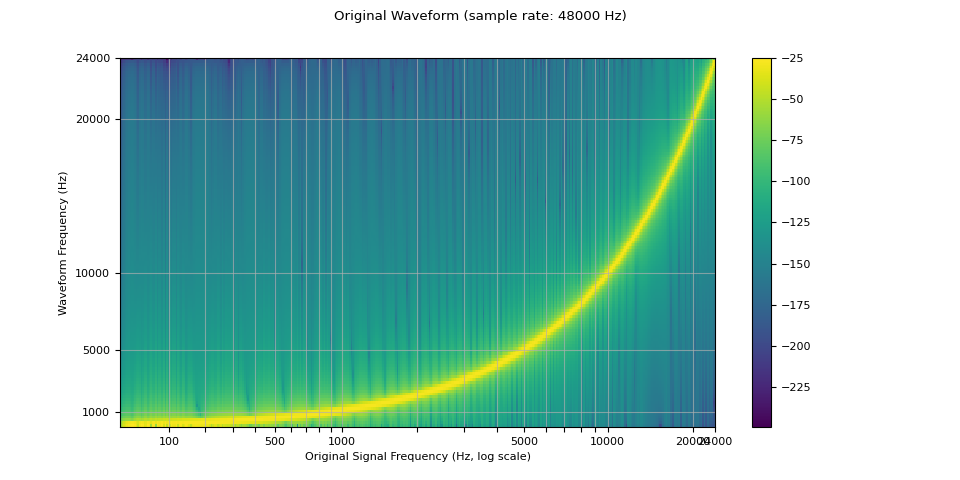
我们看到,在重采样波形的频谱图中,存在原始波形中不存在的伪影。
这种效应称为混叠。 本页解释了它是如何发生的,以及为什么它看起来像反射。
resample_rate = 32000
resampler = T.Resample(sample_rate, resample_rate, dtype=waveform.dtype)
resampled_waveform = resampler(waveform)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Resampled Waveform")
Audio(resampled_waveform.numpy()[0], rate=resample_rate)
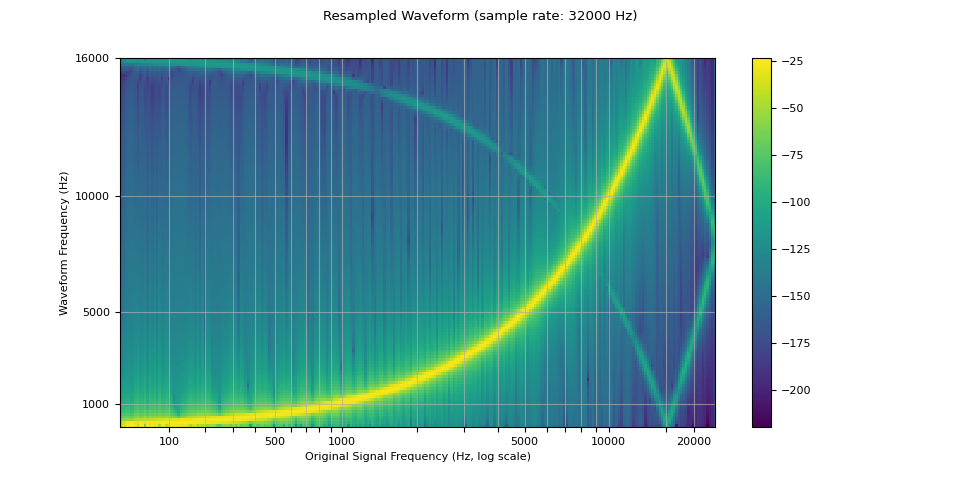
使用参数控制重采样质量
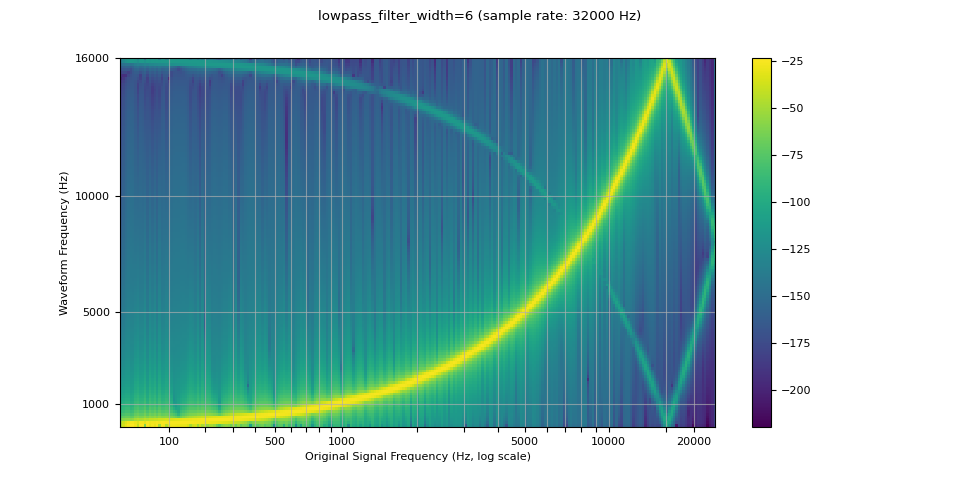
Lowpass filter width
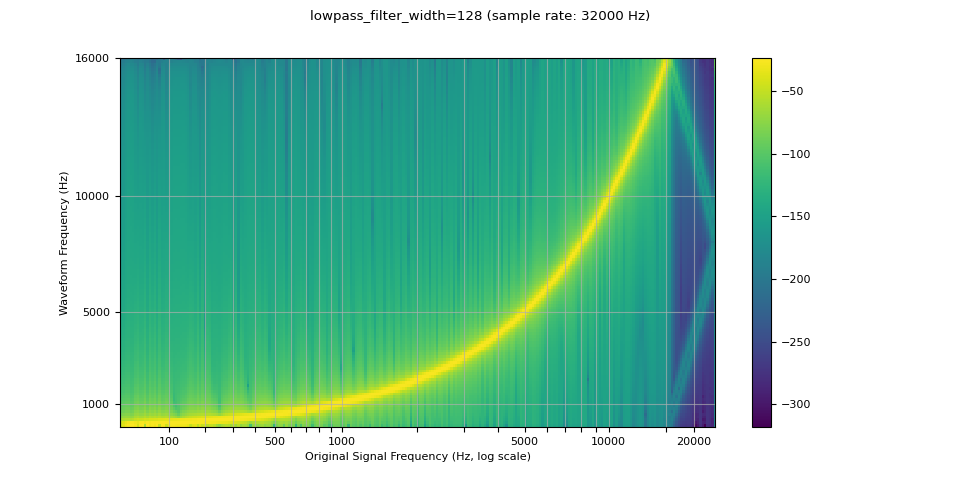
由于用于插值的滤波器无限扩展,因此 lowpass_filter_width 参数用于控制用于对插值进行加窗的滤波器的宽度。 它也称为过零数,因为插值在每个时间单位都经过零。 使用较大的 lowpass_filter_width 可提供更清晰、更精确的滤波器,但计算成本更高。
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, lowpass_filter_width=6)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="lowpass_filter_width=6")
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, lowpass_filter_width=128)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="lowpass_filter_width=128")
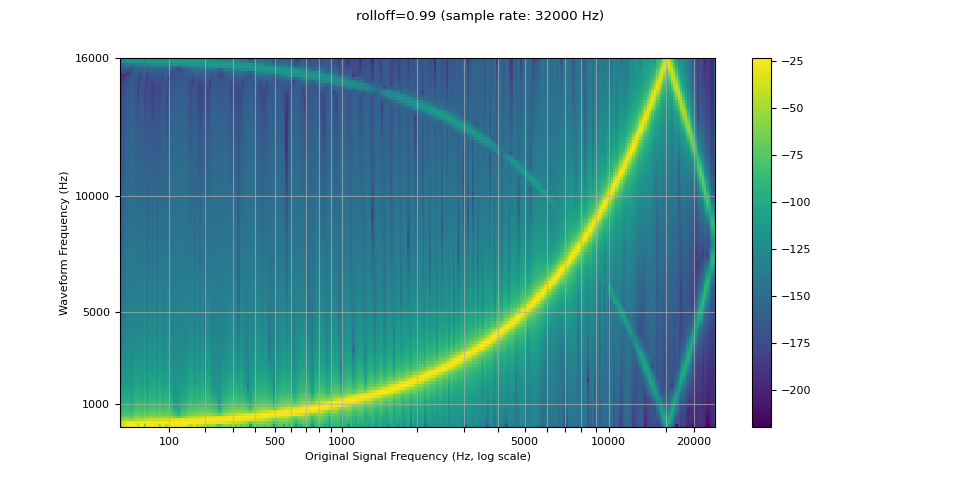
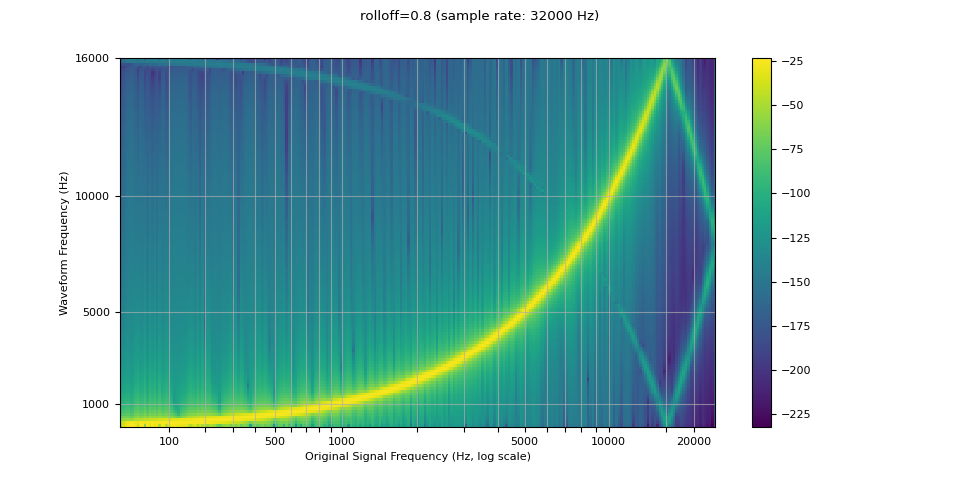
Rolloff
rolloff 参数表示为奈奎斯特频率的一个小数,奈奎斯特频率是给定的有限采样率所能表示的最大频率。rolloff 决定了 lowpass filter 的截止,并控制混叠的程度,当高于奈奎斯特的频率映射到较低的频率时,就会发生混叠。因此,较低的 rolloff 将减少混叠的数量,但它也将减少一些较高的频率。
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, rolloff=0.99)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="rolloff=0.99")
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, rolloff=0.8)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="rolloff=0.8")
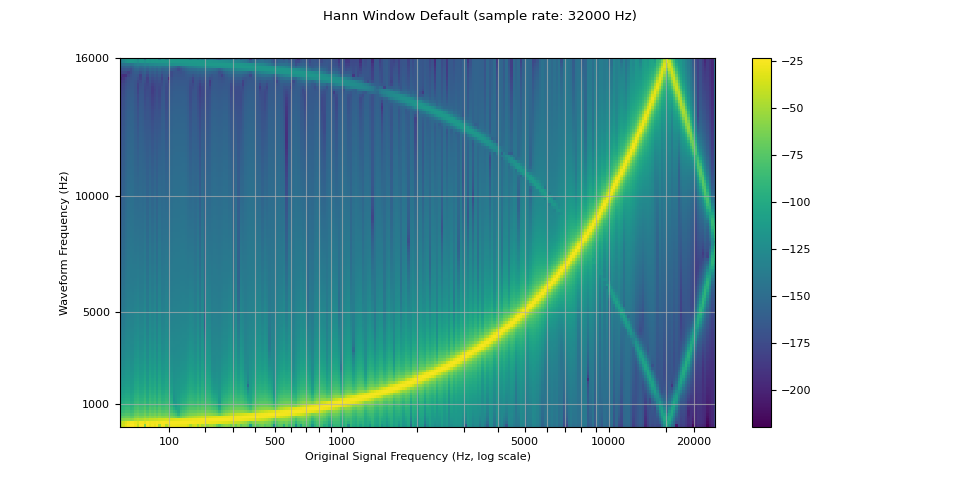
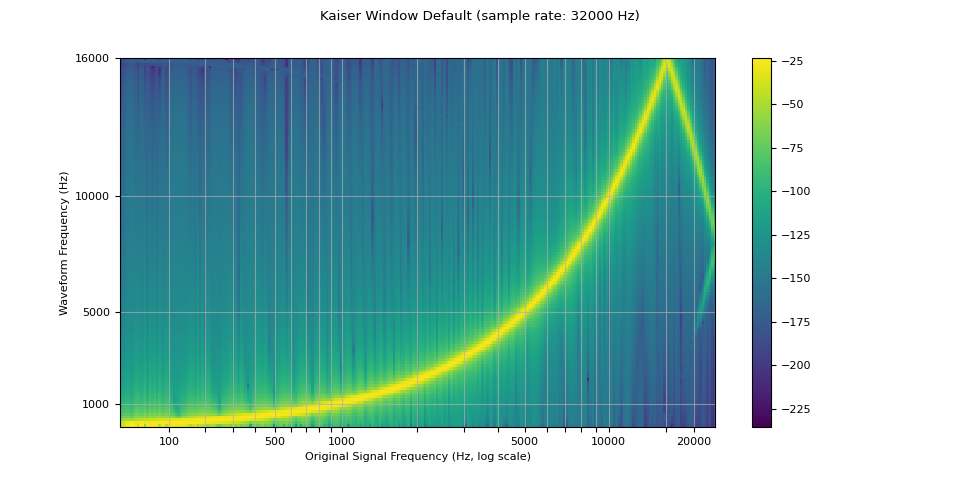
窗口函数
默认情况下,torchaudio 的重采样使用 Hann 窗口滤波器,这是一个加权余弦函数。它还支持凯泽窗(Kaiser window),这是一个近乎最优的窗函数,它包含一个额外的 beta 参数,用于设计滤波器的平滑性和脉冲宽度。这可以使用 resampling_method 参数来控制。
sample_rate = 48000
resample_rate = 32000
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, resampling_method="sinc_interp_hann")
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Hann Window Default")
resampled_waveform = F.resample(waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate, resampling_method="sinc_interp_kaiser")
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Default")
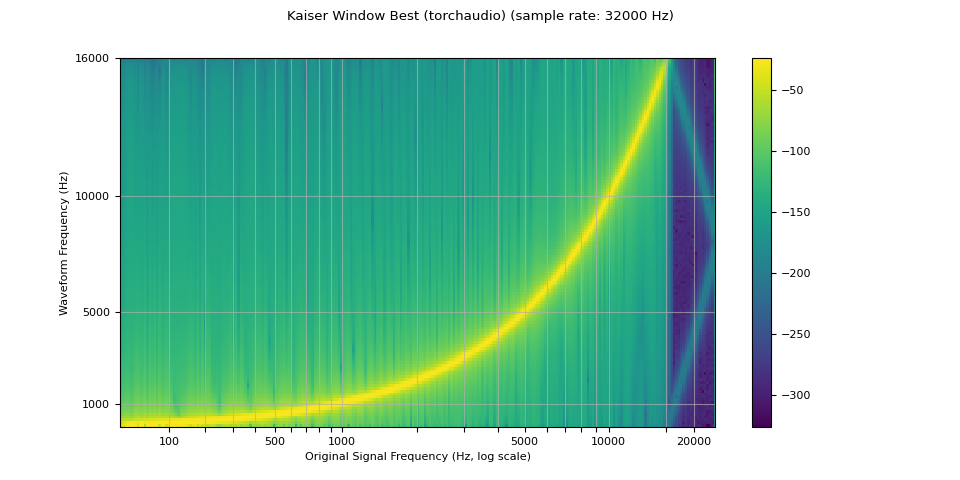
与 librosa 比较
torchaudio 的重采样函数可用于产生类似于 librosa (resampy) 的 kaiser 窗口重采样的结果,但有一些噪声
kaiser_best
resampled_waveform = F.resample(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=64,
rolloff=0.9475937167399596,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_kaiser",
beta=14.769656459379492,
)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Best (torchaudio)")
librosa_resampled_waveform = torch.from_numpy(
librosa.resample(waveform.squeeze().numpy(), orig_sr=sample_rate, target_sr=resample_rate, res_type="kaiser_best")
).unsqueeze(0)
plot_sweep(librosa_resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Best (librosa)")
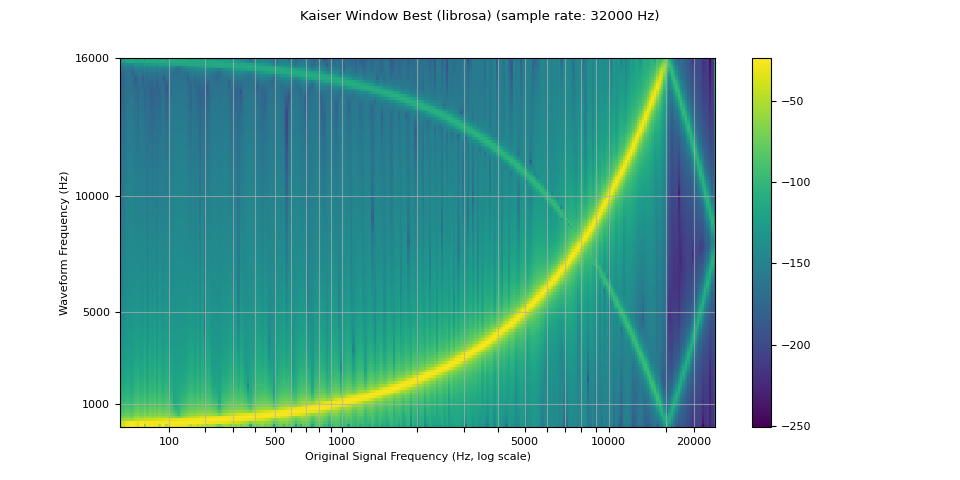
mse = torch.square(resampled_waveform - librosa_resampled_waveform).mean().item()
print("torchaudio and librosa kaiser best MSE:", mse)
输出:
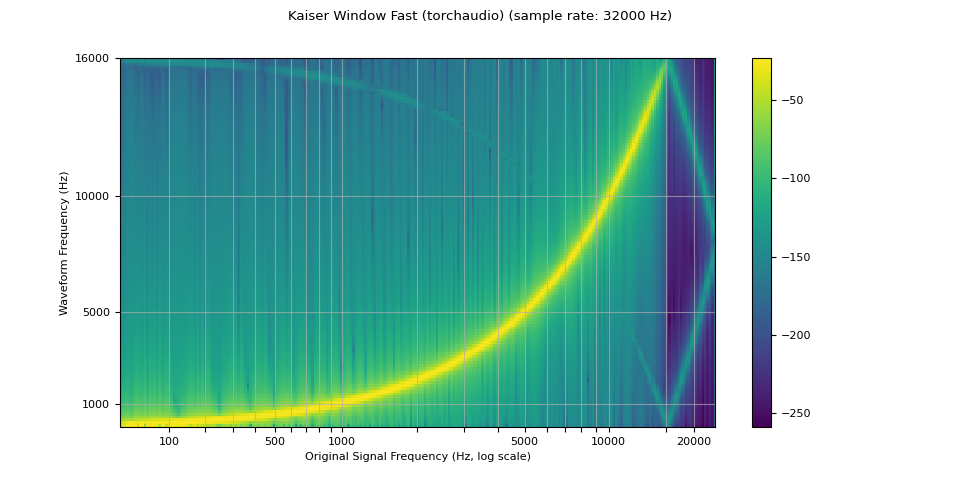
kaiser_fast
resampled_waveform = F.resample(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=16,
rolloff=0.85,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_kaiser",
beta=8.555504641634386,
)
plot_sweep(resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Fast (torchaudio)")
librosa_resampled_waveform = torch.from_numpy(
librosa.resample(waveform.squeeze().numpy(), orig_sr=sample_rate, target_sr=resample_rate, res_type="kaiser_fast")
).unsqueeze(0)
plot_sweep(librosa_resampled_waveform, resample_rate, title="Kaiser Window Fast (librosa)")
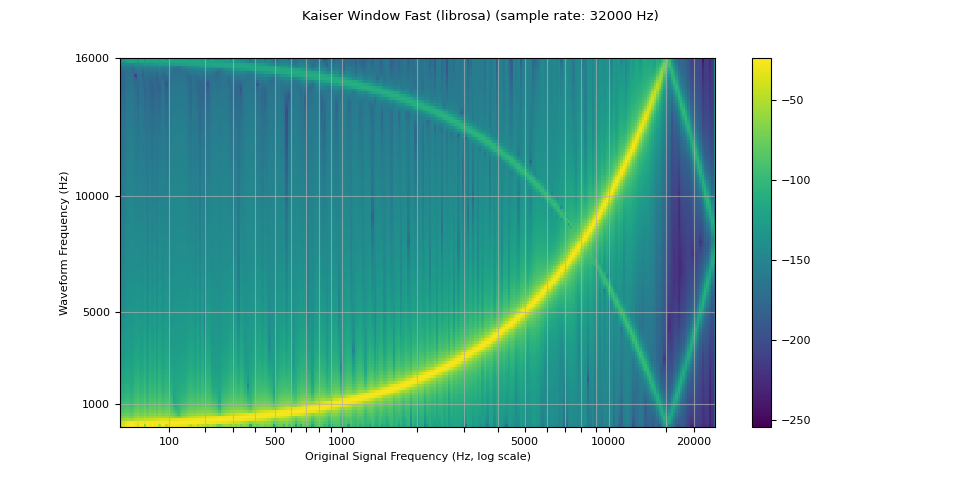
mse = torch.square(resampled_waveform - librosa_resampled_waveform).mean().item()
print("torchaudio and librosa kaiser fast MSE:", mse)
输出:
性能基准测试
下面是两对采样率之间的下采样和上采样波形的基准。我们展示了 lowpass_filter_width、窗口类型和采样率可能产生的性能影响。使用 torchaudio 中相应的参数,与 librosa 的 kaiser_best 和 kaiser_fast 进行比较。
print(f"torchaudio: {torchaudio.__version__}")
print(f"librosa: {librosa.__version__}")
print(f"resampy: {resampy.__version__}")
输出:
def benchmark_resample_functional(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=6,
rolloff=0.99,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_hann",
beta=None,
iters=5,
):
return (
timeit.timeit(
stmt="""
torchaudio.functional.resample(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=lowpass_filter_width,
rolloff=rolloff,
resampling_method=resampling_method,
beta=beta,
)
""",
setup="import torchaudio",
number=iters,
globals=locals(),
)
* 1000
/ iters
)
def benchmark_resample_transforms(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=6,
rolloff=0.99,
resampling_method="sinc_interp_hann",
beta=None,
iters=5,
):
return (
timeit.timeit(
stmt="resampler(waveform)",
setup="""
import torchaudio
resampler = torchaudio.transforms.Resample(
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
lowpass_filter_width=lowpass_filter_width,
rolloff=rolloff,
resampling_method=resampling_method,
dtype=waveform.dtype,
beta=beta,
)
resampler.to(waveform.device)
""",
number=iters,
globals=locals(),
)
* 1000
/ iters
)
def benchmark_resample_librosa(
waveform,
sample_rate,
resample_rate,
res_type=None,
iters=5,
):
waveform_np = waveform.squeeze().numpy()
return (
timeit.timeit(
stmt="""
librosa.resample(
waveform_np,
orig_sr=sample_rate,
target_sr=resample_rate,
res_type=res_type,
)
""",
setup="import librosa",
number=iters,
globals=locals(),
)
* 1000
/ iters
)
def benchmark(sample_rate, resample_rate):
times, rows = [], []
waveform = get_sine_sweep(sample_rate).to(torch.float32)
args = (waveform, sample_rate, resample_rate)
# sinc 64 zero-crossings
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, lowpass_filter_width=64)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, lowpass_filter_width=64)
times.append([None, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("sinc (width 64)")
# sinc 6 zero-crossings
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, lowpass_filter_width=16)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, lowpass_filter_width=16)
times.append([None, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("sinc (width 16)")
# kaiser best
kwargs = {
"lowpass_filter_width": 64,
"rolloff": 0.9475937167399596,
"resampling_method": "sinc_interp_kaiser",
"beta": 14.769656459379492,
}
lib_time = benchmark_resample_librosa(*args, res_type="kaiser_best")
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, **kwargs)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, **kwargs)
times.append([lib_time, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("kaiser_best")
# kaiser fast
kwargs = {
"lowpass_filter_width": 16,
"rolloff": 0.85,
"resampling_method": "sinc_interp_kaiser",
"beta": 8.555504641634386,
}
lib_time = benchmark_resample_librosa(*args, res_type="kaiser_fast")
f_time = benchmark_resample_functional(*args, **kwargs)
t_time = benchmark_resample_transforms(*args, **kwargs)
times.append([lib_time, f_time, t_time])
rows.append("kaiser_fast")
df = pd.DataFrame(times, columns=["librosa", "functional", "transforms"], index=rows)
return df
def plot(df):
print(df.round(2))
ax = df.plot(kind="bar")
plt.ylabel("Time Elapsed [ms]")
plt.xticks(rotation=0, fontsize=10)
for cont, col, color in zip(ax.containers, df.columns, mcolors.TABLEAU_COLORS):
label = ["N/A" if v != v else str(v) for v in df[col].round(2)]
ax.bar_label(cont, labels=label, color=color, fontweight="bold", fontsize="x-small")
下采样 (48 -> 44.1 kHz)
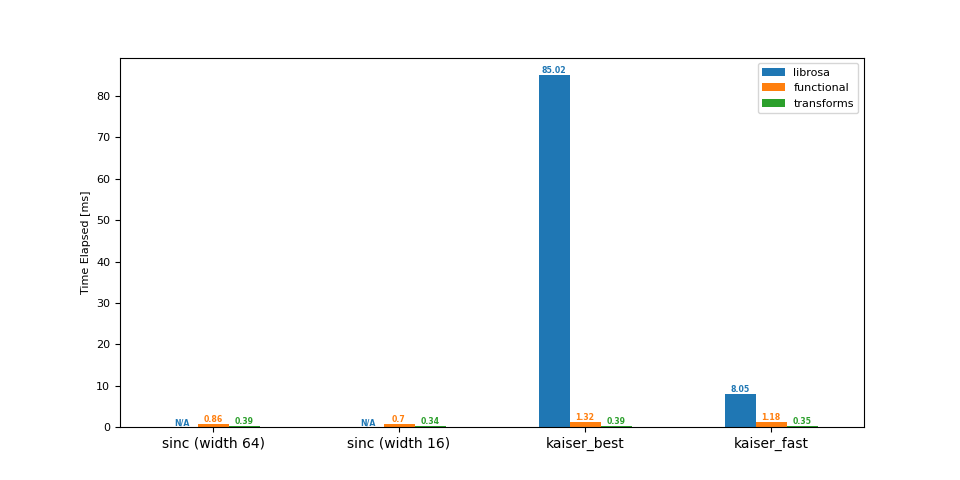
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 0.86 0.39
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.70 0.34
kaiser_best 85.02 1.32 0.39
kaiser_fast 8.05 1.18 0.35
下采样 (16 -> 8 kHz)
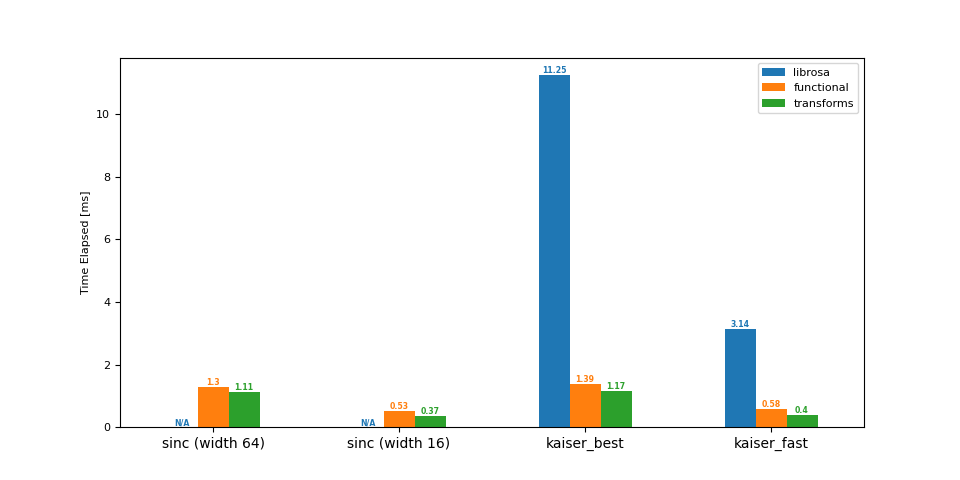
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 1.30 1.11
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.53 0.37
kaiser_best 11.25 1.39 1.17
kaiser_fast 3.14 0.58 0.40
上采样 (44.1 -> 48 kHz)
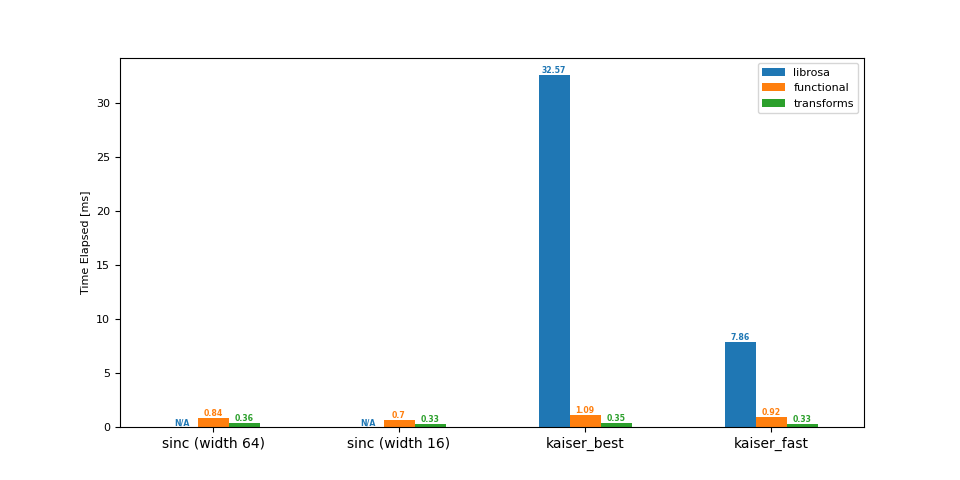
输出:
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 0.84 0.36
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.70 0.33
kaiser_best 32.57 1.09 0.35
kaiser_fast 7.86 0.92 0.33
上采样 (8 -> 16 kHz)
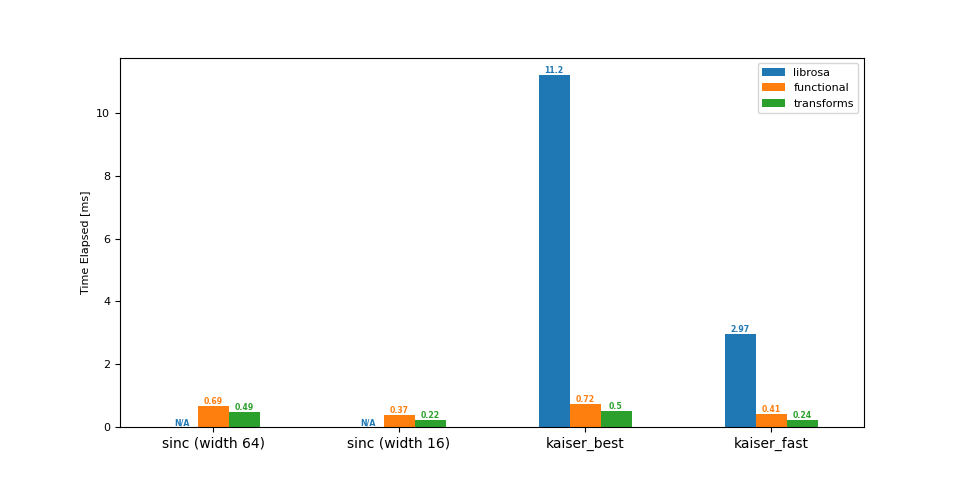
输出:
librosa functional transforms
sinc (width 64) NaN 0.69 0.49
sinc (width 16) NaN 0.37 0.22
kaiser_best 11.20 0.72 0.50
kaiser_fast 2.97 0.41 0.24
总结
详细说明结果:
-
较大的
lowpass_filter_width会导致较大的重采样内核,因此会增加内核计算和卷积的计算时间 -
使用
sinc_interp_kaiser会导致比默认的sinc_interp_hann更长的计算时间,因为计算中间窗口值更复杂 -
采样率和重采样率之间的大 GCD 将导致简化,从而允许更小的内核和更快的内核计算。
脚本总运行时间:(0 分 3.373 秒)

