使用分布式数据并行和管道并行训练 Transformer 模型 ¶
译者:片刻小哥哥
项目地址:https://pytorch.apachecn.org/2.0/tutorials/advanced/ddp_pipeline
原始地址:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/ddp_pipeline.html
作者 : Pritam Damania
本教程演示如何使用 分布式数据并行 和 管道并行性 。本教程是使用 nn.Transformer 和 TorchText 进行序列到序列建模教程的扩展,并扩展了同一模型演示如何使用分布式数据并行和 管道并行来训练 Transformer 模型。
先决条件:
定义模型 ¶
-
PositionalEncoding
模块注入一些有关序列中标记的相对或绝对位置的信息。位置编码与嵌入具有相同的维度,因此可以将两者相加。在这里,我们使用不同频率的
sine
和
cosine
函数。
import sys
import os
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import tempfile
from torch.nn import TransformerEncoder, TransformerEncoderLayer
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, dropout=0.1, max_len=5000):
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, d_model)
position = torch.arange(0, max_len, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(1)
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2).float() * (-math.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0).transpose(0, 1)
self.pe = nn.Parameter(pe, requires_grad=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.pe[:x.size(0), :]
return self.dropout(x)
在本教程中,我们将在两个 GPU 上拆分 Transformer 模型,并使用 管道并行性来训练模型。除此之外,我们还使用分布式数据并行来训练该管道的两个副本。我们有一个进程跨 GPU 0 和 1 驱动管道,另一个进程跨 GPU 2 和 3 驱动管道。然后,这两个进程都使用分布式数据并行来训练两个副本。该模型与 使用 nn.Transformer 和 TorchText 进行序列到序列建模 教程中使用的模型完全相同,但是分为两个阶段。参数数量最多的属于 nn.TransformerEncoder 层。
[nn.TransformerEncoder] ](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.TransformerEncoder.html)
本身由
nlayers
组成
nn.TransformerEncoderLayer
.
因此,我们的重点是
nn.TransformerEncoder
并且我们分割模型
这样一半的\ n nn.TransformerEncoderLayer
位于一个 GPU 上,
另一半位于另一个 GPU 上。为此,我们将
Encoder
和
Decoder
部分提取到单独的模块中,然后构建
nn.Sequential
表示原始 Transformer 模块。
if sys.platform == 'win32':
print('Windows platform is not supported for pipeline parallelism')
sys.exit(0)
if torch.cuda.device_count() < 4:
print('Need at least four GPU devices for this tutorial')
sys.exit(0)
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ntoken, ninp, dropout=0.5):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.pos_encoder = PositionalEncoding(ninp, dropout)
self.encoder = nn.Embedding(ntoken, ninp)
self.ninp = ninp
self.init_weights()
def init_weights(self):
initrange = 0.1
self.encoder.weight.data.uniform_(-initrange, initrange)
def forward(self, src):
# Need (S, N) format for encoder.
src = src.t()
src = self.encoder(src) * math.sqrt(self.ninp)
return self.pos_encoder(src)
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ntoken, ninp):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.decoder = nn.Linear(ninp, ntoken)
self.init_weights()
def init_weights(self):
initrange = 0.1
self.decoder.bias.data.zero_()
self.decoder.weight.data.uniform_(-initrange, initrange)
def forward(self, inp):
# Need batch dimension first for output of pipeline.
return self.decoder(inp).permute(1, 0, 2)
启动多个进程进行训练 ¶
我们启动两个进程,每个进程在两个 GPU 上驱动自己的管道。
每个进程都会执行 run_worker
。
加载并批处理数据 ¶
训练过程使用来自
torchtext
的 Wikitext-2 数据集。
要访问 torchtext 数据集,请按照以下位置的说明安装 torchdata
https://github.com/pytorch/data
。\ n
vocab 对象是基于训练数据集构建的,用于将 token 数值化为tensor。从顺序数据开始,
batchify()
函数将数据集排列成列,在数据被分成大小
batch_size
的批次后,修剪掉剩余的任何标记。\例如,以字母表为序列(总长度为 26)
且批量大小为 4,我们会将字母表分为 4 个
长度为 6 的序列:
[ \begin{bmatrix} \text{A} & \text{B} & \text{C} & \ldots & \text{X} & \text{Y } & \text{Z} \end{bmatrix} \Rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}\text{A} \ \text {B} \ \text{C} \ \text{D} \ \text{E} \ \text{F}\end{bmatrix} & \begin{bmatrix}\text{G} \ \text{H} \ \text{I} \ \text{J} \ \文本{K} \ \文本{L}\结束{bmatrix} & \开始{bmatrix}\文本{M} \ \文本{N} \ \ ext{O} \ \text{P} \ \text{Q} \ \text{R}\end{bmatrix} & \begin{bmatrix} \文本{S} \ \文本{T} \ \文本{U} \ \文本{V} \ \文本{W} \ \text{X}\end{bmatrix} \end{bmatrix}]
这些列被模型视为独立的,这意味着
G 的依赖性
和
F
无法学习,但允许更
高效的批处理。
# In 'run_worker'
def print_with_rank(msg):
print('[RANK {}]: {}'.format(rank, msg))
from torchtext.datasets import WikiText2
from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer
from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator
train_iter = WikiText2(split='train')
tokenizer = get_tokenizer('basic_english')
vocab = build_vocab_from_iterator(map(tokenizer, train_iter), specials=["<unk>"])
vocab.set_default_index(vocab["<unk>"])
def data_process(raw_text_iter):
data = [torch.tensor(vocab(tokenizer(item)), dtype=torch.long) for item in raw_text_iter]
return torch.cat(tuple(filter(lambda t: t.numel() > 0, data)))
train_iter, val_iter, test_iter = WikiText2()
train_data = data_process(train_iter)
val_data = data_process(val_iter)
test_data = data_process(test_iter)
device = torch.device(2 * rank)
def batchify(data, bsz, rank, world_size, is_train=False):
# Divide the dataset into ``bsz`` parts.
nbatch = data.size(0) // bsz
# Trim off any extra elements that wouldn't cleanly fit (remainders).
data = data.narrow(0, 0, nbatch * bsz)
# Evenly divide the data across the ``bsz`` batches.
data = data.view(bsz, -1).t().contiguous()
# Divide the data across the ranks only for training data.
if is_train:
data_per_rank = data.size(0) // world_size
data = data[rank * data_per_rank : (rank + 1) * data_per_rank]
return data.to(device)
batch_size = 20
eval_batch_size = 10
train_data = batchify(train_data, batch_size, rank, world_size, True)
val_data = batchify(val_data, eval_batch_size, rank, world_size)
test_data = batchify(test_data, eval_batch_size, rank, world_size)
get_batch()
函数生成变压器模型的输入和目标序列。它将源数据细分为
length
bptt
的块。对于语言建模任务,模型需要
以下单词作为
Target
。例如,
bptt
值为 2,
we’d 会为
i
= 0 获取以下两个变量:
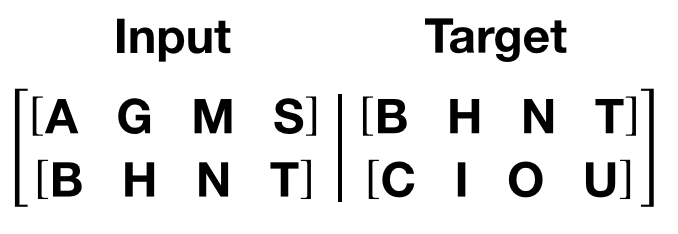
需要注意的是,块沿着维度 0,与
中的
S
维度一致变压器模型。批次维度
N
沿维度 1。
# In 'run_worker'
bptt = 35
def get_batch(source, i):
seq_len = min(bptt, len(source) - 1 - i)
data = source[i:i+seq_len]
target = source[i+1:i+1+seq_len].view(-1)
# Need batch dimension first for pipeline parallelism.
return data.t(), target
模型比例和管道初始化 ¶
为了演示使用管道并行性训练大型 Transformer 模型,
我们适当扩展 Transformer 层。我们使用嵌入维度为 4096、隐藏大小为 4096、16 个注意力头和总共 8 个转换器层 (
nn.TransformerEncoderLayer
)。这将创建一个具有
~10 亿
参数的模型。
我们需要初始化 RPC 框架 因为 Pipe 依赖于 RPC 框架 RRef 允许将来扩展到跨主机管道。由于我们’ 使用单个进程来驱动多个 GPU, 我们只需要使用单个工作线程来初始化 RPC 框架。
然后使用一个 GPU 上的 8 个转换器层和另一个 GPU 上的 8 个转换器层来初始化管道。一个管道跨 GPU 0 和 1 设置,
另一个管道跨 GPU 2 和 3 设置。然后使用
DistributedDataParallel
复制两个管道。
# In 'run_worker'
ntokens = len(vocab) # the size of vocabulary
emsize = 4096 # embedding dimension
nhid = 4096 # the dimension of the feedforward network model in ``nn.TransformerEncoder``
nlayers = 8 # the number of ``nn.TransformerEncoderLayer`` in ``nn.TransformerEncoder``
nhead = 16 # the number of heads in the Multihead Attention models
dropout = 0.2 # the dropout value
from torch.distributed import rpc
tmpfile = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile()
rpc.init_rpc(
name="worker",
rank=0,
world_size=1,
rpc_backend_options=rpc.TensorPipeRpcBackendOptions(
init_method="file://{}".format(tmpfile.name),
# Specifying _transports and _channels is a workaround and we no longer
# will have to specify _transports and _channels for PyTorch
# versions >= 1.8.1
_transports=["ibv", "uv"],
_channels=["cuda_ipc", "cuda_basic"],
)
)
# Number of GPUs for model parallelism.
num_gpus = 2
partition_len = ((nlayers - 1) // num_gpus) + 1
# Add encoder in the beginning.
tmp_list = [Encoder(ntokens, emsize, dropout).cuda(2 * rank)]
module_list = []
# Add all the necessary transformer blocks.
for i in range(nlayers):
transformer_block = TransformerEncoderLayer(emsize, nhead, nhid, dropout)
if i != 0 and i % (partition_len) == 0:
module_list.append(nn.Sequential(*tmp_list))
tmp_list = []
device = i // (partition_len)
tmp_list.append(transformer_block.to(2 * rank + device))
# Add decoder in the end.
tmp_list.append(Decoder(ntokens, emsize).cuda(2 * rank + num_gpus - 1))
module_list.append(nn.Sequential(*tmp_list))
# Need to use 'checkpoint=never' since as of PyTorch 1.8, Pipe checkpointing
# doesn't work with DDP.
from torch.distributed.pipeline.sync import Pipe
chunks = 8
model = Pipe(torch.nn.Sequential(
*module_list), chunks = chunks, checkpoint="never")
# Initialize process group and wrap model in DDP.
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel
import torch.distributed as dist
os.environ['MASTER_ADDR'] = 'localhost'
os.environ['MASTER_PORT'] = '29500'
dist.init_process_group(
backend="nccl", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
model = DistributedDataParallel(model)
def get_total_params(module: torch.nn.Module):
total_params = 0
for param in module.parameters():
total_params += param.numel()
return total_params
print_with_rank('Total parameters in model: {:,}'.format(get_total_params(model)))
运行模型 ¶
CrossEntropyLoss 用于跟踪损失, SGD 实现随机梯度下降法作为优化器。初始 学习率设置为 5.0。 StepLR 应用于 通过纪元调整学习率。在训练过程中,我们使用 nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_ 函数将所有梯度一起缩放以防止爆炸。
# In 'run_worker'
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
lr = 5.0 # learning rate
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, 1.0, gamma=0.95)
import time
def train():
model.train() # Turn on the train mode
total_loss = 0.
start_time = time.time()
ntokens = len(vocab)
# Train only for 50 batches to keep script execution time low.
nbatches = min(50 * bptt, train_data.size(0) - 1)
for batch, i in enumerate(range(0, nbatches, bptt)):
data, targets = get_batch(train_data, i)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Since the Pipe is only within a single host and process the ``RRef``
# returned by forward method is local to this node and can simply
# retrieved via ``RRef.local_value()``.
output = model(data).local_value()
# Need to move targets to the device where the output of the
# pipeline resides.
loss = criterion(output.view(-1, ntokens), targets.cuda(2 * rank + 1))
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 0.5)
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
log_interval = 10
if batch % log_interval == 0 and batch > 0:
cur_loss = total_loss / log_interval
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print_with_rank('| epoch {:3d} | {:5d}/{:5d} batches | '
'lr {:02.2f} | ms/batch {:5.2f} | '
'loss {:5.2f} | ppl {:8.2f}'.format(
epoch, batch, nbatches // bptt, scheduler.get_last_lr()[0],
elapsed * 1000 / log_interval,
cur_loss, math.exp(cur_loss)))
total_loss = 0
start_time = time.time()
def evaluate(eval_model, data_source):
eval_model.eval() # Turn on the evaluation mode
total_loss = 0.
ntokens = len(vocab)
# Evaluate only for 50 batches to keep script execution time low.
nbatches = min(50 * bptt, data_source.size(0) - 1)
with torch.no_grad():
for i in range(0, nbatches, bptt):
data, targets = get_batch(data_source, i)
output = eval_model(data).local_value()
output_flat = output.view(-1, ntokens)
# Need to move targets to the device where the output of the
# pipeline resides.
total_loss += len(data) * criterion(output_flat, targets.cuda(2 * rank + 1)).item()
return total_loss / (len(data_source) - 1)
循环纪元。如果验证损失是迄今为止我们’见过的最好的,则保存模型。在每个时期后调整学习率。
# In 'run_worker'
best_val_loss = float("inf")
epochs = 3 # The number of epochs
best_model = None
for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
epoch_start_time = time.time()
train()
val_loss = evaluate(model, val_data)
print_with_rank('-' * 89)
print_with_rank('| end of epoch {:3d} | time: {:5.2f}s | valid loss {:5.2f} | '
'valid ppl {:8.2f}'.format(epoch, (time.time() - epoch_start_time),
val_loss, math.exp(val_loss)))
print_with_rank('-' * 89)
if val_loss < best_val_loss:
best_val_loss = val_loss
best_model = model
scheduler.step()
使用测试数据集评估模型 ¶
应用最佳模型来检查测试数据集的结果。
# In 'run_worker'
test_loss = evaluate(best_model, test_data)
print_with_rank('=' * 89)
print_with_rank('| End of training | test loss {:5.2f} | test ppl {:8.2f}'.format(
test_loss, math.exp(test_loss)))
print_with_rank('=' * 89)
# Main execution
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
if __name__=="__main__":
world_size = 2
mp.spawn(run_worker, args=(world_size, ), nprocs=world_size, join=True)
输出 ¶
[RANK 0]: | epoch 1 | 10/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 778.97 | loss 43.31 | ppl 6432469059895903232.00
[RANK 1]: | epoch 1 | 10/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 778.90 | loss 44.50 | ppl 21245447128217366528.00
[RANK 0]: | epoch 1 | 20/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 699.89 | loss 44.50 | ppl 21176949187407757312.00
[RANK 1]: | epoch 1 | 20/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 699.87 | loss 44.62 | ppl 23975861229620961280.00
[RANK 0]: | epoch 1 | 30/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 698.86 | loss 41.62 | ppl 1193312915629888256.00
[RANK 1]: | epoch 1 | 30/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 698.87 | loss 40.69 | ppl 471605759847546240.00
[RANK 0]: | epoch 1 | 40/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 698.34 | loss 45.20 | ppl 42812308420836458496.00
[RANK 1]: | epoch 1 | 40/ 50 batches | lr 5.00 | ms/batch 698.33 | loss 45.68 | ppl 68839569686012223488.00
[RANK 1]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 1]: | end of epoch 1 | time: 40.08s | valid loss 0.80 | valid ppl 2.22
[RANK 1]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: | end of epoch 1 | time: 40.09s | valid loss 0.80 | valid ppl 2.22
[RANK 0]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: | epoch 2 | 10/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 768.51 | loss 36.34 | ppl 6063529544668166.00
[RANK 1]: | epoch 2 | 10/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 769.23 | loss 37.41 | ppl 17651211266236086.00
[RANK 0]: | epoch 2 | 20/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 699.57 | loss 28.97 | ppl 3798441739584.11
[RANK 1]: | epoch 2 | 20/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 699.56 | loss 29.28 | ppl 5203636967575.47
[RANK 0]: | epoch 2 | 30/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 699.04 | loss 28.43 | ppl 2212498693571.25
[RANK 1]: | epoch 2 | 30/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 699.05 | loss 28.33 | ppl 2015144761281.48
[RANK 0]: | epoch 2 | 40/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 699.10 | loss 23.30 | ppl 13121380184.92
[RANK 1]: | epoch 2 | 40/ 50 batches | lr 4.75 | ms/batch 699.09 | loss 23.41 | ppl 14653799192.87
[RANK 0]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: | end of epoch 2 | time: 39.97s | valid loss 0.24 | valid ppl 1.27
[RANK 0]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 1]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 1]: | end of epoch 2 | time: 39.98s | valid loss 0.24 | valid ppl 1.27
[RANK 1]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: | epoch 3 | 10/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 769.36 | loss 12.80 | ppl 361681.11
[RANK 1]: | epoch 3 | 10/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 768.97 | loss 12.57 | ppl 287876.61
[RANK 0]: | epoch 3 | 20/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 698.27 | loss 12.01 | ppl 164364.60
[RANK 1]: | epoch 3 | 20/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 698.30 | loss 11.98 | ppl 159095.89
[RANK 0]: | epoch 3 | 30/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 697.75 | loss 10.90 | ppl 54261.91
[RANK 1]: | epoch 3 | 30/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 697.72 | loss 10.89 | ppl 53372.39
[RANK 0]: | epoch 3 | 40/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 699.49 | loss 10.78 | ppl 47948.35
[RANK 1]: | epoch 3 | 40/ 50 batches | lr 4.51 | ms/batch 699.50 | loss 10.79 | ppl 48664.42
[RANK 0]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: | end of epoch 3 | time: 39.96s | valid loss 0.38 | valid ppl 1.46
[RANK 0]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 1]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 1]: | end of epoch 3 | time: 39.96s | valid loss 0.38 | valid ppl 1.46
[RANK 1]: -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[RANK 0]: ===================================================================================
[RANK 0]: | End of training | test loss 0.33 | test ppl 1.39
[RANK 0]: ===================================================================================
[RANK 1]: ===================================================================================
[RANK 1]: | End of training | test loss 0.33 | test ppl 1.39
[RANK 1]: ===================================================================================
脚本的总运行时间: ( 0 分 0.000 秒)

